Recent Posts
It's the recipients
- laura
- May 14, 2015
Most delivery problems to US ISPs boil down to sending mail to people who don’t want it or expect it. Sure, we do technical audits and find issues with how companies are sending mail. But all the technical correctness in the world isn’t going to make up for sending mail users complain about or don’t interact with.
Recently we were working with a client who was having some delivery problems for one mail stream. As we dug down into the issue, we discovered a couple things about the mail stream.
Purchased Lists and ESPs
- laura
- May 14, 2015
After some thought, I’ve decided to remove a few ESPs from this list based on personal experience with them allowing customers to send to purchased lists. If your company has disappeared and you want to come back, you’ll need to actually stop the spam coming from your network. Every company that’s been removed has received a complaint from me specifically mentioning the address was purchased and allowed that same customer to continue spamming the same address. Deal with your spam and we can talk about reinstatement.
Read MoreiCloud Postmaster resources
- steve
- May 12, 2015
iCloud Mail (mac.com, me.com, icloud.com) has a shiny, new postmaster resources page. No whitelist, no FBL, just a good list of best practices to follow for sending bulk mail.
Read MoreWhat is the Mail From field?
- josh
- May 8, 2015
When emails are sent, there are two from fields, the Mail From and the Display From address. The Display From address (technically referred to as RFC.5322 from address) is the from address that is displayed to the end user within their email client. The Mail From (technically referred to as RFC.5321 from address) is the email address to which bounce messages are delivered. The Mail From field is sometimes referred to as the Return Path address, Envelope From address, or Bounce address.
It may seem confusing to have an email with two from fields, but knowing the difference is important to properly setup your SPF records.
Taking a look at this email I received from GoPro, the Return-Path (5321.From) goes back to @bounce.email.gopro.com. If I were to reply to the email, the message would go to @email.gopro.com. The Display From (5322.From) address is gopro@email.gopro.com.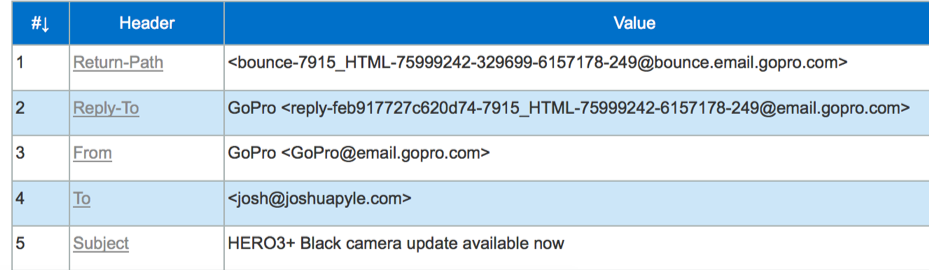
I would want to add the email address GoPro@email.gopro.com to my address book because that is the email address that is displayed in my email client. The reason why the Return-Path is different from the From address is because GoPro likely has an automated system that will process the bounce back messages (sent to @bounce.email.gopro.com) and automatically flag or unsubscribe those email addresses. This allows GoPro to setup automatic processing of the different mail streams sent to them, one stream being the bounce backs after a mailing and the second being an automated customer service system.
Where does SPF fit in?
SPF checks the Mail From (5321.From) address, not the Display From (5322.From) address. In the example above, there should be an SPF record for the subdomain of bounce.email.gopro.com. I can check the SPF record using our Authentication tools http://tools.wordtothewise.com/spf/check/bounce.email.gopro.com and I receive the following results: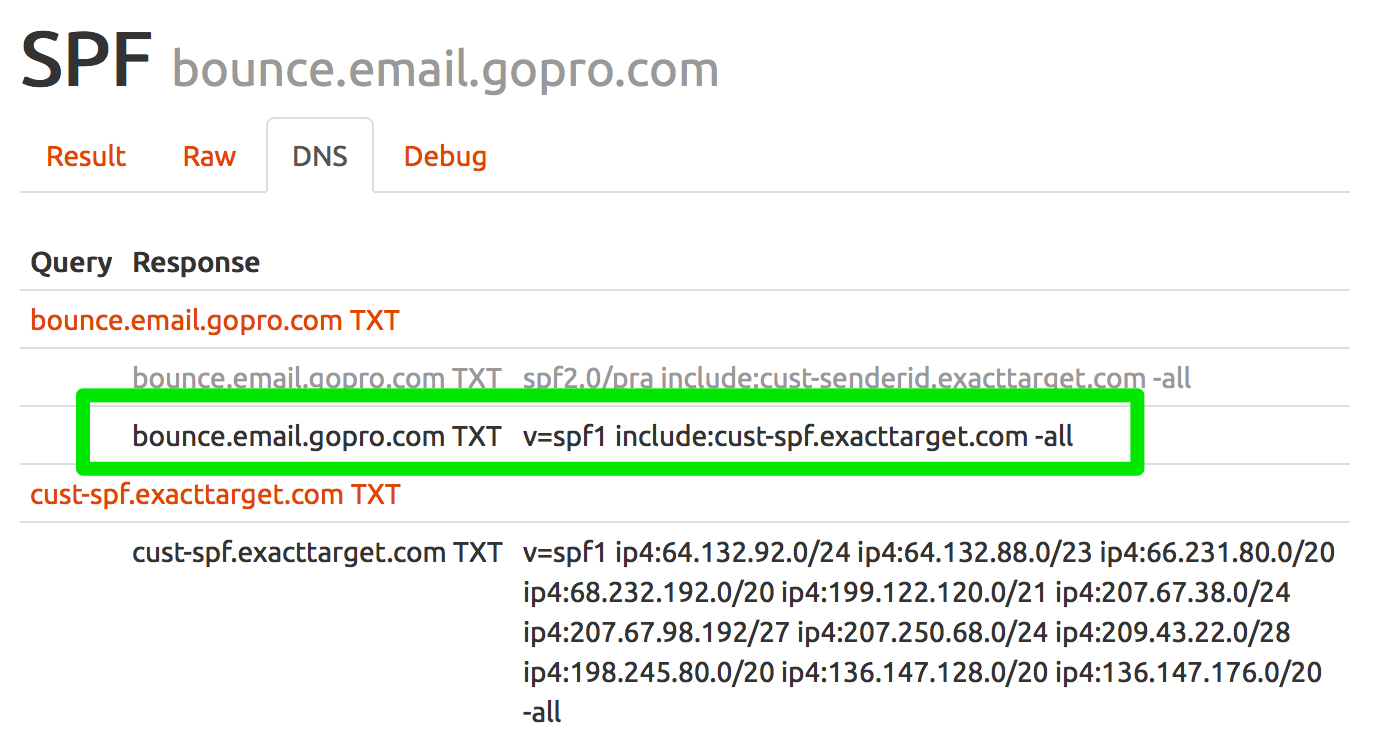
Checking the headers shows that GoPro does have a SPF record setup and the message was authenticated with SPF.![]()
For SPF records, make sure the SPF record matches the Mail From (From.5321)/Return-Path domain name. Have your recipients add the Display From (From.5322) email address to their address book so they will continue to receive your mailings.
4 things spammers do legitimate marketers don't
- laura
- May 7, 2015
I’ve never met a spammer that claims to be a spammer. Most that I’ve met claim to be legitimate marketers (or high volume email deployers). But there are things spammers do that I never expect to see a legitimate marketer doing.
I’ve written about these things throughout the blog (tag: TWSD), but it’s probably time to actually pull them together into a single post.
Four things to check before your next mailing
- laura
- May 5, 2015
Like many bits of technology, email is often set-and-forget. Everything is checked and rechecked during setup, and then no one goes back and looks at it again. But mail programs are not static, and people make changes. These changes don’t really break things, but over time they can create their own set of problems.
Setting aside some time every quarter or even every year to check and make sure all the bits of mail are configured correctly is a good idea.
April 2015: The Month in Email
- laura
- May 4, 2015
We started the month with some conversations about best practices, both generally looking at the sort of best practices people follow (or don’t) as well as some specific practices we wanted to look at in more depth. Three for this month:
Read MoreOffice365/EOP and Outlook.com/Hotmail will converge
- josh
- May 1, 2015
Terry Zink posted two informative blog posts recently, the first being the change to unauthenticated mail sent over IPv6 to EOP and the second post about EOP (Office365 and Exchange Hosting) and Outlook.com/Hotmail infrastructure converging.
Exchange Online Protection (EOP) is the filtering system in place for Office 365 and hosted Exchange customers. Outlook.com/Hotmail utilized its own mail filtering system and provides SNDS/JMRP programs. EOP is setup for redundancy, failover, provides geo-region servers to serve customers, and has supported TLS for over a decade. Terry explains that Hotmail’s spam filtering technology is more advanced than EOP’s, but EOP’s backend platform is more advanced. The process to convert Outlook.com/Hotmail to use EOP’s filtering system started six months ago and is still a work in progress. Once completed, Outlook.com/Hotmail and Office365/EOP will share the same UX look and feel. The anti-spam technologies will be able to be shared between the two as they will share the same backend infrastructure.
Some of the challenges of merging the two systems include:
Categories
Tags
- 2010
- 2016
- 2fa
- 419
- 4xx
- 554
- 5xx
- @
- Aarp
- Abacus
- Abandoned
- Aboutmyemail
- Abuse
- Abuse Desk
- Abuse Enforcement
- Abuse Prevention
- Academia
- Accreditation
- Acme
- Acquisition
- Address Book
- Addresses
- Administrivia
- Adsp
- Advanced Delivery
- Advertiser
- Advertising
- Advice
- Affiliate
- Affiliates
- After the Email
- Alerts
- Algorithm
- Alice
- Alignment
- Allcaps
- Alt Text
- AMA
- Amazon
- Amp
- Amsterdam
- Analysis
- Anecdotes
- Anti-Spam
- Anti-Spam Laws
- Anti-Spammers
- Antwort
- AOL
- Appeals
- Appearances
- Appending
- Apple
- Arc
- Arf
- Arrest
- Arrests
- Ascii
- Asides
- Ask Laura
- Askwttw
- Assertion
- Assumptions
- ATT
- Attacks
- Attention
- Attrition
- Audit
- Authentication
- Authentication. BT
- Autonomous
- Award
- B2B
- B2C
- Backhoe
- Backscatter
- Backus-Naur Form
- Banks
- Barracuda
- Barry
- Base64
- Base85
- Bcc
- Bcp
- Bear
- Bears
- Behaviour
- Benchmark
- BESS
- Best Practices
- Bgp
- BIMI
- Bit Rot
- Bitly
- Bizanga
- Black Friday
- Blackfriday
- Blacklist
- Blacklists
- Blast
- Blo
- Block
- Blockin
- Blocking
- Blocklist
- Blocklisting
- Blocklists
- Blocks
- Blog
- Blog Links
- Blogroll
- Blogs
- Bob
- Boca
- Bofa
- Book Review
- Bot
- Botnet
- Botnets
- Bots
- Bounce
- Bounce Handling
- Bounces
- Branding
- Brands
- Breach
- Breaches
- Breech
- Bronto
- Browser
- Bsi
- Bucket
- Bulk
- Bulk Folder
- Bulk Mail
- Business
- Business Filters
- Buying Leads
- Buying Lists
- C-28
- CA
- Caa
- Cabbage
- Cache
- Cadence
- CAH
- California
- Campaign
- CAN SPAM
- Canada
- Candy
- Candycandycandy
- Canonicalization
- Canspam
- Captcha
- Career Developmnent
- Careers at WttW
- Cargo Cult
- Case Law
- Cases
- CASL
- Cat
- Cbl
- CDA
- Cert
- Certification
- CFL
- CFWS
- Change
- Charter
- Cheat
- Cheese
- Choicepoint
- Choochoo
- Christmas
- Chrome
- Cidr
- Cisco
- Civil
- Clear.net
- Clearwire.net
- Cli
- Click
- Click Through
- Click Tracking
- Clicks
- Clickthrough
- Client
- Cloudflare
- Cloudmark
- Cname
- Co-Reg
- Co-Registration
- Cocktail
- Code
- COI
- Comcast
- Comments
- Commercial
- Communication
- Community
- Comodo
- Comparison
- Competitor
- Complaint
- Complaint Rates
- Complaints
- Compliancce
- Compliance
- Compromise
- Conference
- Conferences
- Confirmation
- Confirmed (Double) Opt-In
- Confirmed Opt-In
- Congress
- Consent
- Conservatives
- Consistency
- Constant Contact
- Consultants
- Consulting
- Content
- Content Filters
- Contracts
- Cookie
- Cookie Monster
- COPL
- Corporate
- Cost
- Court Ruling
- Cox
- Cox.net
- Cpanel
- Crib
- Crime
- CRM
- Crowdsource
- Crtc
- Cryptography
- CSRIC
- CSS
- Curl
- Customer
- Cyber Monday
- Czar
- Data
- Data Hygiene
- Data Security
- Data Segmentation
- Data Verification
- DBL
- Dbp
- Ddos
- Dea
- Dead Addresses
- Dedicated
- Dedicated IPs
- Defamation
- Deferral
- Definitions
- Delays
- Delisting
- Deliverability
- Deliverability Experts
- Deliverability Improvement
- Deliverability Summit
- Deliverability Week
- Deliverability Week 2024
- Deliverabiltiy
- DeliverabiltyWeek
- Delivery Blog Carnival
- Delivery Discussion
- Delivery Emergency
- Delivery Experts
- Delivery Improvement
- Delivery Lore
- Delivery News
- Delivery Problems
- Dell
- Design
- Desks
- Dhs
- Diagnosis
- Diff
- Dig
- Direct Mag
- Direct Mail
- Directives
- Discounts
- Discovery
- Discussion Question
- Disposable
- Dk
- DKIM
- Dkimcore
- DMA
- DMARC
- DNS
- Dnsbl
- Dnssec
- Docs
- Doingitright
- Domain
- Domain Keys
- Domain Reputation
- DomainKeys
- Domains
- Domains by Proxy
- Dontpanic
- Dot Stuffing
- Dotcom
- Double Opt-In
- Dublin
- Dyn
- Dynamic Email
- E360
- Earthlink
- Ec2
- Ecoa
- Economics
- ECPA
- Edatasource
- Edns0
- Eec
- Efail
- Efax
- Eff
- Election
- Email Address
- Email Addresses
- Email Change of Address
- Email Client
- Email Design
- Email Formats
- Email Marketing
- Email Strategy
- Email Verification
- Emailappenders
- Emailgeeks
- Emails
- Emailstuff
- Emoji
- Emoticon
- Encert
- Encryption
- End User
- Endusers
- Enforcement
- Engagement
- Enhanced Status Code
- Ennui
- Entrust
- Eol
- EOP
- Epsilon
- Esp
- ESPC
- ESPs
- EU
- Ev Ssl
- Evaluating
- Events
- EWL
- Exchange
- Excite
- Expectations
- Experience
- Expires
- Expiring
- False Positives
- FAQ
- Fathers Day
- Fbl
- FBL Microsoft
- FBLs
- Fbox
- FCC
- Fcrdns
- Featured
- Fedex
- Feds
- Feedback
- Feedback Loop
- Feedback Loops
- Fiction
- Filter
- Filter Evasion
- Filtering
- Filterings
- Filters
- Fingerprinting
- Firefox3
- First Amendment
- FISA
- Flag Day
- Forensics
- Format
- Formatting
- Forms
- Forwarding
- Fraud
- Freddy
- Frequency
- Friday
- Friday Spam
- Friendly From
- From
- From Address
- FTC
- Fussp
- Gabbard
- GDPR
- Geoip
- Gevalia
- Gfi
- Git
- Giveaway
- Giving Up
- Global Delivery
- Glossary
- Glyph
- Gmail
- Gmails
- Go
- Godaddy
- Godzilla
- Good Email Practices
- Good Emails in the Wild
- Goodmail
- Google Buzz
- Google Postmaster Tools
- Graphic
- GreenArrow
- Greylisting
- Greymail
- Groupon
- GT&U
- Guarantee
- Guest Post
- Guide
- Habeas
- Hack
- Hacking
- Hacks
- Hall of Shame
- Harassment
- Hard Bounce
- Harvesting
- Harvey
- Hash
- Hashbusters
- Headers
- Heartbleed
- Hearts
- HELO
- Help
- Henet
- Highspeedinternet
- Hijack
- History
- Holiday
- Holidays
- Holomaxx
- Hostdns4u
- Hostile
- Hostname
- Hotmail
- How To
- Howto
- Hrc
- Hsts
- HTML
- HTML Email
- Http
- Huey
- Humanity
- Humor
- Humour
- Hygiene
- Hypertouch
- I18n
- ICANN
- Icloud
- IContact
- Identity
- Idiots
- Idn
- Ietf
- Image Blocking
- Images
- Imap
- Inbox
- Inbox Delivery
- Inboxing
- Index
- India
- Indiegogo
- Industry
- Infection
- Infographic
- Information
- Inky
- Inline
- Innovation
- Insight2015
- Integration
- Internationalization
- Internet
- Intuit
- IP
- IP Address
- Ip Addresses
- IP Repuation
- IP Reputation
- IPhone
- IPO
- IPv4
- IPv6
- Ironport
- Ironport Cisco
- ISIPP
- ISP
- ISPs
- J.D. Falk Award
- Jail
- Jaynes
- JD
- Jobs
- Json
- Junk
- Juno/Netzero/UOL
- Key Rotation
- Keybase
- Keynote
- Kickstarter
- Kraft
- Laposte
- Lavabit
- Law
- Laws
- Lawsuit
- Lawsuits
- Lawyer
- Layout
- Lead Gen
- Leak
- Leaking
- Leaks
- Legal
- Legality
- Legitimate Email Marketer
- Letsencrypt
- Letstalk
- Linked In
- Links
- List Hygiene
- List Management
- List Purchases
- List the World
- List Usage
- List-Unsubscribe
- Listing
- Listmus
- Lists
- Litmus
- Live
- Livingsocial
- London
- Lookup
- Lorem Ipsum
- Lycos
- Lyris
- M3AAWG
- Maawg
- MAAWG2007
- Maawg2008
- MAAWG2012
- MAAWGSF
- Machine Learning
- Magill
- Magilla
- Mail Chimp
- Mail Client
- MAIL FROM
- Mail Privacy Protection
- Mail Problems
- Mail.app
- Mail.ru
- Mailboxes
- Mailchimp
- Mailgun
- Mailing Lists
- Mailman
- Mailop
- Mainsleaze
- Maitai
- Malicious
- Malicious Mail
- Malware
- Mandrill
- Maps
- Marketer
- Marketers
- Marketing
- Marketo
- Markters
- Maths
- Mcafee
- Mccain
- Me@privacy.net
- Measurements
- Media
- Meh
- Meltdown
- Meme
- Mentor
- Merry
- Message-ID
- Messagelabs
- MessageSystems
- Meta
- Metric
- Metrics
- Micdrop
- Microsoft
- Milter
- Mime
- Minimal
- Minshare
- Minute
- Mit
- Mitm
- Mobile
- Models
- Monitoring
- Monkey
- Monthly Review
- Mpp
- MSN/Hotmail
- MSN/Hotmail
- MTA
- Mua
- Mutt
- Mx
- Myths
- Myvzw
- Needs Work
- Netcat
- Netsol
- Netsuite
- Network
- Networking
- New Year
- News
- News Articles
- Nhi
- NJABL
- Now Hiring
- NTP
- Nxdomain
- Oath
- Obituary
- Office 365
- Office365
- One-Click
- Only Influencers
- Oops
- Opaque Cookie
- Open
- Open Detection
- Open Rate
- Open Rates
- Open Relay
- Open Tracking
- Opendkim
- Opens
- Openssl
- Opt-In
- Opt-Out
- Optonline
- Oracle
- Outage
- Outages
- Outblaze
- Outlook
- Outlook.com
- Outrage
- Outreach
- Outsource
- Ownership
- Owning the Channel
- P=reject
- Pacer
- Pander
- Panel
- Password
- Patent
- Paypal
- PBL
- Penkava
- Permission
- Personalities
- Personalization
- Personalized
- Pgp
- Phi
- Philosophy
- Phish
- Phishers
- Phishing
- Phising
- Photos
- Pii
- PIPA
- PivotalVeracity
- Pix
- Pluscachange
- Podcast
- Policies
- Policy
- Political Mail
- Political Spam
- Politics
- Porn
- Port25 Blocking
- Postfix
- Postmaster
- Power MTA
- Practices
- Predictions
- Preferences
- Prefetch
- Preview
- Primers
- Privacy
- Privacy Policy
- Privacy Protection
- Private Relay
- Productive Mail
- Promotions
- Promotions Tab
- Proofpoint
- Prospect
- Prospecting
- Protocols
- Proxy
- Psa
- PTR
- Public Suffix List
- Purchased
- Purchased Lists
- Purchases
- Purchasing Lists
- Questions
- Quoted Printable
- Rakuten
- Ralsky
- Rant
- Rate Limiting
- Ray Tomlinson
- Rc4
- RDNS
- Re-Engagement
- Read
- Ready to Post
- Readytopost
- Real People
- Realtime Address Verification
- Recaptcha
- Received
- Receivers
- Recipient
- Recipients
- Redirect
- Redsnapper
- Reference
- Registrar
- Registration
- Rejection
- Rejections
- Rejective
- Relationship
- Relevance
- Relevancy
- Removals
- Render Rate
- Rendering
- Replay
- Repost
- Repudiation
- Reputation
- Requirements
- Research
- Resources
- Responsive
- Responsive Design
- Responsys
- Retail
- Retired Domains
- Retro
- Return Path
- Return Path Certified
- ReturnPath
- Reunion.com
- Reverse Dns
- RFC
- RFC2047
- RFC2821/2822
- RFC5321/5322
- RFC5322
- RFC8058
- RFC821/822
- RFCs
- Roadr
- RoadRunner
- Rodney Joffe
- ROKSO
- Role Accounts
- Rollout
- RPost
- RPZ
- Rule 34
- Rules
- Rum
- Rustock
- S.1618
- SaaS
- Sales
- Salesforce
- Sass
- SBCGlobal
- Sbl
- Scam
- Scammers
- Scams
- Scanning
- Scraping
- Screamer
- Screening
- Script
- Sec
- Secure
- Security
- Segmentation
- Selligent
- Send
- Sender
- Sender Score
- Sender Score Certified
- Senderbase
- Senderid
- Senders
- Senderscore
- Sendgrid
- Sending
- Sendy
- Seo
- Service
- Services
- Ses
- Seth Godin
- SFDC
- SFMAAWG2009
- SFMAAWG2010
- SFMAAWG2014
- Shared
- Shell
- Shouting
- Shovel
- Signing
- Signups
- Silly
- Single Opt-In
- Slack
- Slicing
- Smarthost
- Smiley
- Smime
- SMS
- SMTP
- Snds
- Snowshoe
- Soa
- Socia
- Social Media
- Social Networking
- Soft Bounce
- Software
- Sony
- SOPA
- Sorbs
- Spam
- Spam Blocking
- Spam Definition
- Spam Filtering
- Spam Filters
- Spam Folder
- Spam Law
- Spam Laws
- Spam Reports
- Spam Traps
- Spam. IMessage
- Spamarrest
- Spamassassin
- Spamblocking
- Spamcannibal
- Spamcon
- Spamcop
- Spamfiltering
- Spamfilters
- Spamfolder
- Spamhaus
- Spamhause
- Spammer
- Spammers
- Spammest
- Spamming
- Spamneverstops
- Spamresource
- Spamtrap
- Spamtraps
- Spamza
- Sparkpost
- Speaking
- Special Offers
- Spectre
- SPF
- Spoofing
- SproutDNS
- Ssl
- Standards
- Stanford
- Starttls
- Startup
- State Spam Laws
- Statistics
- Storm
- Strategy
- Stunt
- Subject
- Subject Lines
- Subscribe
- Subscriber
- Subscribers
- Subscription
- Subscription Process
- Success Stories
- Suing
- Suppression
- Surbl
- Sureclick
- Suretymail
- Survey
- Swaks
- Syle
- Symantec
- Tabbed Inbox
- Tabs
- Tagged
- Tagging
- Target
- Targeting
- Techincal
- Technical
- Telnet
- Template
- Tempo
- Temporary
- Temporary Failures
- Terminology
- Testing
- Text
- Thanks
- This Is Spam
- Throttling
- Time
- Timely
- TINS
- TLD
- Tlp
- TLS
- TMIE
- Tmobile
- Too Much Mail
- Tool
- Tools
- Toomuchemail
- Tor
- Trademark
- Traffic Light Protocol
- Tragedy of the Commons
- Transactional
- Transition
- Transparency
- Traps
- Travel
- Trend/MAPS
- Trend Micro
- Trend/MAPS
- Trigger
- Triggered
- Troubleshooting
- Trustedsource
- TWSD
- Txt
- Types of Email
- Typo
- Uce
- UCEprotect
- Unblocking
- Uncategorized
- Undisclosed Recipients
- Unexpected Email
- Unicode
- Unroll.me
- Unsolicited
- Unsubcribe
- Unsubscribe
- Unsubscribed
- Unsubscribes
- Unsubscribing
- Unsubscription
- Unwanted
- URIBL
- Url
- Url Shorteners
- Usenet
- User Education
- Utf8
- Valentine's Day
- Validation
- Validity
- Value
- Valueclick
- Verification
- Verizon
- Verizon Media
- VERP
- Verticalresponse
- Vetting
- Via
- Video
- Violence
- Virginia
- Virtumundo
- Virus
- Viruses
- Vmc
- Vocabulary
- Vodafone
- Volume
- Vzbv
- Wanted Mail
- Warmup
- Weasel
- Webinar
- Webmail
- Weekend Effect
- Welcome Emails
- White Space
- Whitelisting
- Whois
- Wiki
- Wildcard
- Wireless
- Wiretapping
- Wisewednesday
- Women of Email
- Woof
- Woot
- Wow
- Wtf
- Wttw in the Wild
- Xbl
- Xfinity
- Xkcd
- Yahoo
- Yahoogle
- Yogurt
- Zoidberg
- Zombie
- Zombies
- Zoominfo
- Zurb