Recent Posts
Yahoo FBL problems
- laura
- May 21, 2014
Multiple ESPs are reporting that the volume of Yahoo! FBL reports have slowed to a trickle over the last 24 or so hours. While we don’t know exactly what is going on yet, or if it’s on track for being fixed, there does seem to be a problem.
There has been some ongoing maintenance issues with the Yahoo! FBL, where requests for updates and changes weren’t being handled in a timely fashion. Informed speculation was the resources needed to fix the FBL modification weren’t available. The interesting question is if Y! will commit the resources to fix the FBL. I could make arguments either way. But Yahoo! gets the benefit of the this-is-spam button whether or not they send a complaint back to the sender.
5/21 5pm: Both Yahoo and Return Path (who administer the Y! FBL) are aware of the problem and are working on it.
5/21 6:30pm: Reports are flowing again according to multiple sources.
It's about the spam
- laura
- May 20, 2014
Tell someone they have hit a spamtrap and they go through a typical reaction cycle.
Denial: I didn’t hit a trap! I only send opt-in mail. There must be some mistake. I’m a legitimate company, not a spammer!
Anger: What do you mean that I can’t send mail until I’ve fixed the problem? There is no problem! You can’t stop me from mailing. I’m following the law. My mail is important. I’ll sue.
Bargaining: What if I just send mail to some recipients? What if I hire an email hygiene company to remove traps from my list?
Acceptance: What can I do to make sure the people I’m mailing actually want to be on my list?
Overall, my problem with the focus on spamtraps (and complaints to a lesser extent) is that these metrics are proxies. Spamtraps are a way to objectively monitor incoming email. Mail sent to spamtraps is, demonstrably, sent without permission of the address owner. This doesn’t mean all mail from the same source is spam, but there is proof at least some of the mail is spam.
If there is enough bad mail on that list, then reworking the subscription process may be necessary to fix delivery.
Emoji – older than you think
- steve
- May 16, 2014

It might just be random 17th Century punctuation, but this poem from 1648 certainly seems to be using a smiley face emoji.
(OK, it’s probably not intentional, but it’s lovely intersection of the emoji and the word.)
TLS and Encryption
- steve
- May 15, 2014
Yesterday I talked about STARTTLS deployment, and how it was a good thing to support to help protect the privacy of your recipients.
STARTTLS is just one aspect of protecting email from eavesdropping; encrypting traffic as the mail is being sent or read and encrypting the message itself using PGP or S/MIME are others. This table shows what approaches protect messages at different stages of the messages life:
[table nl=”~”]
Compromise point,SUBMIT~+IMAPS,TLS,PGP /~SMIME
Sender’s computer as mail is sent,,,
Sender’s computer later,,,[icon name=check-square]
Sender’s network,[icon name=check-square],,[icon name=check-square]
Sender’s ISP,,,[icon name=check-square]
Global Internet (passive),,[icon name=check-square],[icon name=check-square]
Global Internet (active),,[icon name=question-circle],[icon name=check-square]
Global Internet (later),,[icon name=question-circle],[icon name=check-square]
3rd party mail services,,,[icon name=check-square]
Recipient’s ISP,,,[icon name=check-square]
Recipient’s network,[icon name=check-square],,[icon name=check-square]
Recipient’s computer as mail is read,,,
Recipient’s computer later,,,[icon name=check-square]
[/table]
You can see that if you’re sending really sensitive data, you should be encrypting the entire message with PGP or S/MIME (or not sending the message via email at all). Doing so will protect the content of the mail against pretty most sorts of attack, but is pretty intrusive for the sender and recipient so can’t really be used without prior agreement with the recipient.
The other approaches will make some sorts of passive surveillance much more difficult, though.
Encrypting the connection a user uses to send mail ([rfc 6409]using the SUBMIT protocol[/rfc]) and to read mail ([rfc 2595]using TLS to protect IMAP or POP3[/rfc]) will protect against passive sniffing when the user is on possibly hostile network, such as public wifi or an employers network. That’s an easy place to try and sniff traffic, and if that traffic isn’t protected an attacker can not only read someone’s email, they can steal their credentials and cause all sorts of havoc. All general purpose mail clients and all ISPs support encryption here, so it’s almost universally used.
STARTTLS use with SMTP is all about protecting email traffic when it’s being sent between ISPs – both between the sender’s ISP and the recipient’s and also between any 3rd party mail services (outsourced spam filtering, mailing list providers, vanity domain fowarders, etc.).
I’ve listed three different sorts of attack on that inter-ISP traffic – passive, active and “later”.
A passive attack is where the attacker has the ability to listen to bytes as they go by, but isn’t able to modify or intercept them. While you might think of this as something a nation state would do, via secret agreements with backbone providers or high-tech fiber optic cable taps, there are ways a smaller attacker might be able to compromise an intermediate router and tap that traffic with little risk of detection. Deploying any sort of STARTTLS will protect against this, even if it’s misconfigured, using expired certificates or even just the default setup of a newly deployed mailserver. Facebook describe these weaker forms of STARTTLS as “opportunistic” in their survey – it’s not perfect, but it’s a lot better than nothing.
An active attack is one where the attacker has the ability to intercept and modify traffic between the two ISPs. This seems like it would be harder to do than a passive attack, but it’s often easier, though not as stealthy. Once that’s done, the attacker can pretend to be the recipient ISP and have full access to read, modify or discard messages. To protect against this sort of attack TLS needs to be used not just to encrypt the traffic in-flight, but also to allow the sender to validate that the mailserver they’re talking to really is who they think it is. This is what Facebook describe as “strict” – it requires that the mailserver have a valid certificate, issued by a legitimate certification authority for the domain that the mail is being sent to.
What about “later”? It’s easy to imagine a case where an attacker has been passively monitoring and recording encrypted traffic for a while, and then later they manage to acquire the encryption keys that were used (by, for example, issuing a subpoena to the recipient ISP, or using a compromise to rip them out of your servers memory). With many forms of encryption once you have those private keys it’s possible to decrypt all the traffic you’ve already captured. There are a few algorithms, though, that have what’s known as perfect forward secrecy – knowing the private keys that were used at the time the mail was transferred doesn’t allow you to decrypt them at a later time. If you’re concerned about the privacy of your messages, you should definitely read up on how to set that up.
All of these techniques are a great way to defend against ubiquitous or casual attempts to read your messages, but none of them are proof against a determined attacker. If all else fails, there’s always a wrench attack.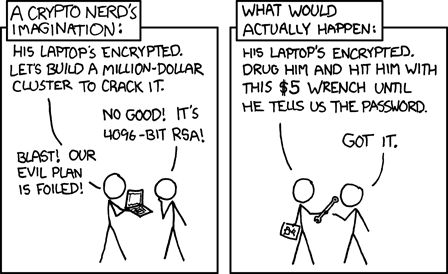
Protect your email with TLS
- steve
- May 14, 2014
You probably use TLS hundreds of times a day. If you don’t recognize the term, you might know it better by it’s older name, SSL.
TLS is what protects your data in transit whenever you go to Google, or Yahoo or even this blog. The little padlock in your browser address bar tells you that your browser has used the TLS protocol to do two things. First, it’s decided that the server you’re connecting to really is operated by Google, or Yahoo or us – you’re (probably) not having your session intercepted by someone in the middle between you and the webserver, either to read your traffic or modify it en-route. Second, it is encrypting all the traffic between you and the webserver, so that it can’t be passively monitored while in transit. Because of concerns about ubiquitous surveillance many websites – including ours – are moving to use TLS for everything, not just for protecting a login page or a credit card number.
That’s great for the web, but how does it apply to email? One place it’s used is for connections between your mail client and your local mailserver – sending mail to the smarthost via [rfc 4409]SUBMIT[/rfc] and fetching mail using [rfc 2595]IMAP or POP3[/rfc] almost always use TLS. That protects the privacy of your messages between you and your ISP and also protects the username and password you use to authenticate with.
Mail traveling between ISPs didn’t used to be encrypted “on the wire” , but about 15 years ago [rfc 3207]an extension to SMTP was proposed[/rfc] that would allow ISPs to negotiate during each session whether they should encrypt it or not. This extension, often referred to as STARTTLS after the command it uses, allows gradual rollout of encryption of mail traffic between ISPs without requiring any sort of flag day. A mailserver that supports STARTTLS will tell everyone who connects to it “Hey! I support STARTTLS!”. When a smarthost that also supports it connects to that mailserver it will go “Great! I support STARTTLS too! Lets do this!” and convert the plain text SMTP session into an encrypted session protected by TLS.
Fifteen years seems like a long period in Internet time, but non-intrusive protocol changes can take a long time to deploy. Facebook Engineering have done the work to see how that deployment is going with their survey of the current state of SMTP STARTTLS deployment. The results are really quite positive – over three quarters of the mailservers they sent mail to supported STARTTLS, covering nearly 60% of their users. That’s definitely enough to make supporting STARTTLS worthwhile.
More about TLS and encryption tomorrow.
Spam is not a valid marketing strategy
- laura
- May 13, 2014
This seems like an attempt to create the next big viral marketing campaign. It’s just spam, though, and not even good spam. There’s nothing about a random “click here” that will entice me to click on it.
Scammers? Spammers? Whoever Ryann Rasmussen at HighSpeedInternet is, she might want to rethink her marketing strategy. It looks more like an infection attempt than anything else.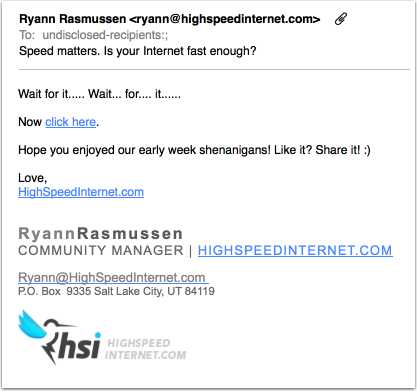
I guess we can say that their mail made an impression, a very negative impression. There is no website at http://highspeedinternet.com. The whois record for highspeedinternet.com is behind domains by proxy. The mail violates CAN SPAM. The address was scraped off our website.
Not all spammers are dodgy Russians. Some spammers are from Utah.
SMTP Level Rejections
- steve
- May 12, 2014
While discussing a draft of a Deliverability BCP document the issue came up of what rejections at different phases of the email delivery transaction can mean. That’s quite a big subject, but here’s a quick cheat sheet.
At initial connection
Dropped or failed connection:
Using Google to taunt coworkers
- laura
- May 9, 2014
Happy Friday, all. This has been a rough week for so many people, I thought we needed a little humor.
From Tim Norton (@norton_tim) on Twitter.
IP reputation and email delivery
- laura
- May 9, 2014
IP reputation is a measure of how much wanted mail a particular IP address sends. This wanted mail is measured as a portion of the total email sent from that IP. Initially IP reputation was really the be all and end all of reputation, there was no real good way to authenticate a domain or a from address. Many ISPs built complex IP reputation models to evaluate mail based on the IP that sent the mail.
These IP reputation models were the best we had, but there were a lot of ways for spammers to game the system. Some spammers would create lots of accounts at ISPs and use them to open and interact with mail. Other spammers would trickle their mail out over hundreds or thousands of IPs in the hopes of diluting the badness enough to get to the inbox. Through it all they kept trying to get mail out through reputable ESPs, either by posing as legitimate customers or compromising servers.
These things worked for a while, but the ISPs started looking harder at the recipient pool in order to figure out if the interactions were real or not. They started looking at the total amount of identical mail coming from multiple IP addresses. The ISPs couldn’t rely on IP reputation so they started to dig down and get into content based filtering.
As the ISPs got better at identifying content and filtering on factors other than source IP, the importance of the IP address on inbox delivery changed. No longer was it good enough to have a high reputation IP sending mail.
These days your IP reputation dictates how fast you can send mail to a particular ISP. But a high reputation IP isn’t sufficient to get all the mail in the inbox. It’s really content that drives the inbox / bulk folder decisions these days.
Generally IPs that the ISP has not seen email traffic from before start out with a slight negative reputation. This is because most new IPs are actually infected machines. The negative reputation translates to rate limiting. The rate limiting minimizes people getting spam while the ISP works out if this is a real sender or a spammer.
Some ISPs put mail in the inbox and bulk foldering during the whitelisting process. In this case what they’re doing is seeing if your recipients care enough about your mail to look for it in the bulk folder. If they do, and they mark the mail as “not spam” then this feeds back to the sender reputation and the IP reputation.
If you’re seeing a lot of bulk foldering of mail, it’s unlikely there’s anything IP reputation based to do. Instead of worrying about IP reputation, focus instead on the content of the mail and see what you may need to do to improve the reputation of the domains and URLs (or landing pages) in the emails.
Categories
Tags
- 2010
- 2016
- 2fa
- 419
- 4xx
- 554
- 5xx
- @
- Aarp
- Abacus
- Abandoned
- Aboutmyemail
- Abuse
- Abuse Desk
- Abuse Enforcement
- Abuse Prevention
- Academia
- Accreditation
- Acme
- Acquisition
- Address Book
- Addresses
- Administrivia
- Adsp
- Advanced Delivery
- Advertiser
- Advertising
- Advice
- Affiliate
- Affiliates
- After the Email
- Alerts
- Algorithm
- Alice
- Alignment
- Allcaps
- Alt Text
- AMA
- Amazon
- Amp
- Amsterdam
- Analysis
- Anecdotes
- Anti-Spam
- Anti-Spam Laws
- Anti-Spammers
- Antwort
- AOL
- Appeals
- Appearances
- Appending
- Apple
- Arc
- Arf
- Arrest
- Arrests
- Ascii
- Asides
- Ask Laura
- Askwttw
- Assertion
- Assumptions
- ATT
- Attacks
- Attention
- Attrition
- Audit
- Authentication
- Authentication. BT
- Autonomous
- Award
- B2B
- B2C
- Backhoe
- Backscatter
- Backus-Naur Form
- Banks
- Barracuda
- Barry
- Base64
- Base85
- Bcc
- Bcp
- Bear
- Bears
- Behaviour
- Benchmark
- BESS
- Best Practices
- Bgp
- BIMI
- Bit Rot
- Bitly
- Bizanga
- Black Friday
- Blackfriday
- Blacklist
- Blacklists
- Blast
- Blo
- Block
- Blockin
- Blocking
- Blocklist
- Blocklisting
- Blocklists
- Blocks
- Blog
- Blog Links
- Blogroll
- Blogs
- Bob
- Boca
- Bofa
- Book Review
- Bot
- Botnet
- Botnets
- Bots
- Bounce
- Bounce Handling
- Bounces
- Branding
- Brands
- Breach
- Breaches
- Breech
- Bronto
- Browser
- Bsi
- Bucket
- Bulk
- Bulk Folder
- Bulk Mail
- Business
- Business Filters
- Buying Leads
- Buying Lists
- C-28
- CA
- Caa
- Cabbage
- Cache
- Cadence
- CAH
- California
- Campaign
- CAN SPAM
- Canada
- Candy
- Candycandycandy
- Canonicalization
- Canspam
- Captcha
- Career Developmnent
- Careers at WttW
- Cargo Cult
- Case Law
- Cases
- CASL
- Cat
- Cbl
- CDA
- Cert
- Certification
- CFL
- CFWS
- Change
- Charter
- Cheat
- Cheese
- Choicepoint
- Choochoo
- Christmas
- Chrome
- Cidr
- Cisco
- Civil
- Clear.net
- Clearwire.net
- Cli
- Click
- Click Through
- Click Tracking
- Clicks
- Clickthrough
- Client
- Cloudflare
- Cloudmark
- Cname
- Co-Reg
- Co-Registration
- Cocktail
- Code
- COI
- Comcast
- Comments
- Commercial
- Communication
- Community
- Comodo
- Comparison
- Competitor
- Complaint
- Complaint Rates
- Complaints
- Compliancce
- Compliance
- Compromise
- Conference
- Conferences
- Confirmation
- Confirmed (Double) Opt-In
- Confirmed Opt-In
- Congress
- Consent
- Conservatives
- Consistency
- Constant Contact
- Consultants
- Consulting
- Content
- Content Filters
- Contracts
- Cookie
- Cookie Monster
- COPL
- Corporate
- Cost
- Court Ruling
- Cox
- Cox.net
- Cpanel
- Crib
- Crime
- CRM
- Crowdsource
- Crtc
- Cryptography
- CSRIC
- CSS
- Curl
- Customer
- Cyber Monday
- Czar
- Data
- Data Hygiene
- Data Security
- Data Segmentation
- Data Verification
- DBL
- Dbp
- Ddos
- Dea
- Dead Addresses
- Dedicated
- Dedicated IPs
- Defamation
- Deferral
- Definitions
- Delays
- Delisting
- Deliverability
- Deliverability Experts
- Deliverability Improvement
- Deliverability Summit
- Deliverability Week
- Deliverability Week 2024
- Deliverabiltiy
- DeliverabiltyWeek
- Delivery Blog Carnival
- Delivery Discussion
- Delivery Emergency
- Delivery Experts
- Delivery Improvement
- Delivery Lore
- Delivery News
- Delivery Problems
- Dell
- Design
- Desks
- Dhs
- Diagnosis
- Diff
- Dig
- Direct Mag
- Direct Mail
- Directives
- Discounts
- Discovery
- Discussion Question
- Disposable
- Dk
- DKIM
- Dkimcore
- DMA
- DMARC
- DNS
- Dnsbl
- Dnssec
- Docs
- Doingitright
- Domain
- Domain Keys
- Domain Reputation
- DomainKeys
- Domains
- Domains by Proxy
- Dontpanic
- Dot Stuffing
- Dotcom
- Double Opt-In
- Dublin
- Dyn
- Dynamic Email
- E360
- Earthlink
- Ec2
- Ecoa
- Economics
- ECPA
- Edatasource
- Edns0
- Eec
- Efail
- Efax
- Eff
- Election
- Email Address
- Email Addresses
- Email Change of Address
- Email Client
- Email Design
- Email Formats
- Email Marketing
- Email Strategy
- Email Verification
- Emailappenders
- Emailgeeks
- Emails
- Emailstuff
- Emoji
- Emoticon
- Encert
- Encryption
- End User
- Endusers
- Enforcement
- Engagement
- Enhanced Status Code
- Ennui
- Entrust
- Eol
- EOP
- Epsilon
- Esp
- ESPC
- ESPs
- EU
- Ev Ssl
- Evaluating
- Events
- EWL
- Exchange
- Excite
- Expectations
- Experience
- Expires
- Expiring
- False Positives
- FAQ
- Fathers Day
- Fbl
- FBL Microsoft
- FBLs
- Fbox
- FCC
- Fcrdns
- Featured
- Fedex
- Feds
- Feedback
- Feedback Loop
- Feedback Loops
- Fiction
- Filter
- Filter Evasion
- Filtering
- Filterings
- Filters
- Fingerprinting
- Firefox3
- First Amendment
- FISA
- Flag Day
- Forensics
- Format
- Formatting
- Forms
- Forwarding
- Fraud
- Freddy
- Frequency
- Friday
- Friday Spam
- Friendly From
- From
- From Address
- FTC
- Fussp
- Gabbard
- GDPR
- Geoip
- Gevalia
- Gfi
- Git
- Giveaway
- Giving Up
- Global Delivery
- Glossary
- Glyph
- Gmail
- Gmails
- Go
- Godaddy
- Godzilla
- Good Email Practices
- Good Emails in the Wild
- Goodmail
- Google Buzz
- Google Postmaster Tools
- Graphic
- GreenArrow
- Greylisting
- Greymail
- Groupon
- GT&U
- Guarantee
- Guest Post
- Guide
- Habeas
- Hack
- Hacking
- Hacks
- Hall of Shame
- Harassment
- Hard Bounce
- Harvesting
- Harvey
- Hash
- Hashbusters
- Headers
- Heartbleed
- Hearts
- HELO
- Help
- Henet
- Highspeedinternet
- Hijack
- History
- Holiday
- Holidays
- Holomaxx
- Hostdns4u
- Hostile
- Hostname
- Hotmail
- How To
- Howto
- Hrc
- Hsts
- HTML
- HTML Email
- Http
- Huey
- Humanity
- Humor
- Humour
- Hygiene
- Hypertouch
- I18n
- ICANN
- Icloud
- IContact
- Identity
- Idiots
- Idn
- Ietf
- Image Blocking
- Images
- Imap
- Inbox
- Inbox Delivery
- Inboxing
- Index
- India
- Indiegogo
- Industry
- Infection
- Infographic
- Information
- Inky
- Inline
- Innovation
- Insight2015
- Integration
- Internationalization
- Internet
- Intuit
- IP
- IP Address
- Ip Addresses
- IP Repuation
- IP Reputation
- IPhone
- IPO
- IPv4
- IPv6
- Ironport
- Ironport Cisco
- ISIPP
- ISP
- ISPs
- J.D. Falk Award
- Jail
- Jaynes
- JD
- Jobs
- Json
- Junk
- Juno/Netzero/UOL
- Key Rotation
- Keybase
- Keynote
- Kickstarter
- Kraft
- Laposte
- Lavabit
- Law
- Laws
- Lawsuit
- Lawsuits
- Lawyer
- Layout
- Lead Gen
- Leak
- Leaking
- Leaks
- Legal
- Legality
- Legitimate Email Marketer
- Letsencrypt
- Letstalk
- Linked In
- Links
- List Hygiene
- List Management
- List Purchases
- List the World
- List Usage
- List-Unsubscribe
- Listing
- Listmus
- Lists
- Litmus
- Live
- Livingsocial
- London
- Lookup
- Lorem Ipsum
- Lycos
- Lyris
- M3AAWG
- Maawg
- MAAWG2007
- Maawg2008
- MAAWG2012
- MAAWGSF
- Machine Learning
- Magill
- Magilla
- Mail Chimp
- Mail Client
- MAIL FROM
- Mail Privacy Protection
- Mail Problems
- Mail.app
- Mail.ru
- Mailboxes
- Mailchimp
- Mailgun
- Mailing Lists
- Mailman
- Mailop
- Mainsleaze
- Maitai
- Malicious
- Malicious Mail
- Malware
- Mandrill
- Maps
- Marketer
- Marketers
- Marketing
- Marketo
- Markters
- Maths
- Mcafee
- Mccain
- Me@privacy.net
- Measurements
- Media
- Meh
- Meltdown
- Meme
- Mentor
- Merry
- Message-ID
- Messagelabs
- MessageSystems
- Meta
- Metric
- Metrics
- Micdrop
- Microsoft
- Milter
- Mime
- Minimal
- Minshare
- Minute
- Mit
- Mitm
- Mobile
- Models
- Monitoring
- Monkey
- Monthly Review
- Mpp
- MSN/Hotmail
- MSN/Hotmail
- MTA
- Mua
- Mutt
- Mx
- Myths
- Myvzw
- Needs Work
- Netcat
- Netsol
- Netsuite
- Network
- Networking
- New Year
- News
- News Articles
- Nhi
- NJABL
- Now Hiring
- NTP
- Nxdomain
- Oath
- Obituary
- Office 365
- Office365
- One-Click
- Only Influencers
- Oops
- Opaque Cookie
- Open
- Open Detection
- Open Rate
- Open Rates
- Open Relay
- Open Tracking
- Opendkim
- Opens
- Openssl
- Opt-In
- Opt-Out
- Optonline
- Oracle
- Outage
- Outages
- Outblaze
- Outlook
- Outlook.com
- Outrage
- Outreach
- Outsource
- Ownership
- Owning the Channel
- P=reject
- Pacer
- Pander
- Panel
- Password
- Patent
- Paypal
- PBL
- Penkava
- Permission
- Personalities
- Personalization
- Personalized
- Pgp
- Phi
- Philosophy
- Phish
- Phishers
- Phishing
- Phising
- Photos
- Pii
- PIPA
- PivotalVeracity
- Pix
- Pluscachange
- Podcast
- Policies
- Policy
- Political Mail
- Political Spam
- Politics
- Porn
- Port25 Blocking
- Postfix
- Postmaster
- Power MTA
- Practices
- Predictions
- Preferences
- Prefetch
- Preview
- Primers
- Privacy
- Privacy Policy
- Privacy Protection
- Private Relay
- Productive Mail
- Promotions
- Promotions Tab
- Proofpoint
- Prospect
- Prospecting
- Protocols
- Proxy
- Psa
- PTR
- Public Suffix List
- Purchased
- Purchased Lists
- Purchases
- Purchasing Lists
- Questions
- Quoted Printable
- Rakuten
- Ralsky
- Rant
- Rate Limiting
- Ray Tomlinson
- Rc4
- RDNS
- Re-Engagement
- Read
- Ready to Post
- Readytopost
- Real People
- Realtime Address Verification
- Recaptcha
- Received
- Receivers
- Recipient
- Recipients
- Redirect
- Redsnapper
- Reference
- Registrar
- Registration
- Rejection
- Rejections
- Rejective
- Relationship
- Relevance
- Relevancy
- Removals
- Render Rate
- Rendering
- Replay
- Repost
- Repudiation
- Reputation
- Requirements
- Research
- Resources
- Responsive
- Responsive Design
- Responsys
- Retail
- Retired Domains
- Retro
- Return Path
- Return Path Certified
- ReturnPath
- Reunion.com
- Reverse Dns
- RFC
- RFC2047
- RFC2821/2822
- RFC5321/5322
- RFC5322
- RFC8058
- RFC821/822
- RFCs
- Roadr
- RoadRunner
- Rodney Joffe
- ROKSO
- Role Accounts
- Rollout
- RPost
- RPZ
- Rule 34
- Rules
- Rum
- Rustock
- S.1618
- SaaS
- Sales
- Salesforce
- Sass
- SBCGlobal
- Sbl
- Scam
- Scammers
- Scams
- Scanning
- Scraping
- Screamer
- Screening
- Script
- Sec
- Secure
- Security
- Segmentation
- Selligent
- Send
- Sender
- Sender Score
- Sender Score Certified
- Senderbase
- Senderid
- Senders
- Senderscore
- Sendgrid
- Sending
- Sendy
- Seo
- Service
- Services
- Ses
- Seth Godin
- SFDC
- SFMAAWG2009
- SFMAAWG2010
- SFMAAWG2014
- Shared
- Shell
- Shouting
- Shovel
- Signing
- Signups
- Silly
- Single Opt-In
- Slack
- Slicing
- Smarthost
- Smiley
- Smime
- SMS
- SMTP
- Snds
- Snowshoe
- Soa
- Socia
- Social Media
- Social Networking
- Soft Bounce
- Software
- Sony
- SOPA
- Sorbs
- Spam
- Spam Blocking
- Spam Definition
- Spam Filtering
- Spam Filters
- Spam Folder
- Spam Law
- Spam Laws
- Spam Reports
- Spam Traps
- Spam. IMessage
- Spamarrest
- Spamassassin
- Spamblocking
- Spamcannibal
- Spamcon
- Spamcop
- Spamfiltering
- Spamfilters
- Spamfolder
- Spamhaus
- Spamhause
- Spammer
- Spammers
- Spammest
- Spamming
- Spamneverstops
- Spamresource
- Spamtrap
- Spamtraps
- Spamza
- Sparkpost
- Speaking
- Special Offers
- Spectre
- SPF
- Spoofing
- SproutDNS
- Ssl
- Standards
- Stanford
- Starttls
- Startup
- State Spam Laws
- Statistics
- Storm
- Strategy
- Stunt
- Subject
- Subject Lines
- Subscribe
- Subscriber
- Subscribers
- Subscription
- Subscription Process
- Success Stories
- Suing
- Suppression
- Surbl
- Sureclick
- Suretymail
- Survey
- Swaks
- Syle
- Symantec
- Tabbed Inbox
- Tabs
- Tagged
- Tagging
- Target
- Targeting
- Techincal
- Technical
- Telnet
- Template
- Tempo
- Temporary
- Temporary Failures
- Terminology
- Testing
- Text
- Thanks
- This Is Spam
- Throttling
- Time
- Timely
- TINS
- TLD
- Tlp
- TLS
- TMIE
- Tmobile
- Too Much Mail
- Tool
- Tools
- Toomuchemail
- Tor
- Trademark
- Traffic Light Protocol
- Tragedy of the Commons
- Transactional
- Transition
- Transparency
- Traps
- Travel
- Trend/MAPS
- Trend Micro
- Trend/MAPS
- Trigger
- Triggered
- Troubleshooting
- Trustedsource
- TWSD
- Txt
- Types of Email
- Typo
- Uce
- UCEprotect
- Unblocking
- Uncategorized
- Undisclosed Recipients
- Unexpected Email
- Unicode
- Unroll.me
- Unsolicited
- Unsubcribe
- Unsubscribe
- Unsubscribed
- Unsubscribes
- Unsubscribing
- Unsubscription
- Unwanted
- URIBL
- Url
- Url Shorteners
- Usenet
- User Education
- Utf8
- Valentine's Day
- Validation
- Validity
- Value
- Valueclick
- Verification
- Verizon
- Verizon Media
- VERP
- Verticalresponse
- Vetting
- Via
- Video
- Violence
- Virginia
- Virtumundo
- Virus
- Viruses
- Vmc
- Vocabulary
- Vodafone
- Volume
- Vzbv
- Wanted Mail
- Warmup
- Weasel
- Webinar
- Webmail
- Weekend Effect
- Welcome Emails
- White Space
- Whitelisting
- Whois
- Wiki
- Wildcard
- Wireless
- Wiretapping
- Wisewednesday
- Women of Email
- Woof
- Woot
- Wow
- Wtf
- Wttw in the Wild
- Xbl
- Xfinity
- Xkcd
- Yahoo
- Yahoogle
- Yogurt
- Zoidberg
- Zombie
- Zombies
- Zoominfo
- Zurb