Recent Posts
Does volume cause blocking?
- laura
- Oct 8, 2014
There seems to be a never ending debate about volume and how it affects delivery and revenue. I regularly get questions asking if ISPs block senders just for volume.
The answer is no. Unless you’re actually sending enough mail to overwhelm the incoming infrastructure, something that’s difficult on today’s internet, you’re unlikely to be blocked due to simply sending a high volume of mail.
Sending mail recipients don’t want, or mail that looks like spam, that will get the mail blocked or filtered.
Yahoo.com on FCC wireless "do not mail" list
- laura
- Oct 7, 2014
Update: As of mid-morning pacific time on 10/7 yahoo.com has been removed from the FCC list.
As part of CAN SPAM the FCC maintains a list of wireless domains that require proof of permission to send mail to. Recently, various email folks noticed that yahoo.com was added to this list.
According to the law, senders have 30 days to meet the permission standards for any recipients at domains on the FCC list. In practical terms what this means is that the FCC and Yahoo have 30 days to fix this error and get yahoo.com off the list. Based on conversations with people who’ve talked to Yahoo and the FCC this is in the process of happening.
This isn’t the first time a non-wireless domain has been added to the FCC list.
As a sender what should you do with your yahoo.com subscribers?
Right now, nothing. There is a 30 day grace period between when a domain goes on the FCC list and when senders need to comply. I have every expectation that this will be removed in less than 30 days.
But what if it’s not?
In that case you will need to segregate out yahoo.com subscribers in 30 days and not mail them until the domain is removed from the FCC list. While I can’t actively suggest ignoring the law, it’s unlikely that the FCC is going to start coming after senders for mailing yahoo.com addresses once the 30 days are up.
More information: Al Iverson’s Spam Resource.
Email marketing not dead yet
- laura
- Oct 6, 2014
If Forrester research is to be believe, email marketing is feeling better. In fact, it seems email marketing is more effective than ever.
Read MoreMarketing pet peeves
- laura
- Oct 3, 2014
Loren McDonald has a great post over at Mediapost listing his email marketing pet peeves. I particularly love this because he includes those things annoy him as a subscriber.
Most of what annoys me as a subscriber is sloppy marketing. Really is it so hard to actually check what you’re sending and who you’re sending it to?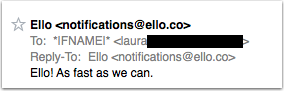
This was a notice from Ello telling me that they’d get to my request for an account “at some point.” There were two fails here. The first is very obvious from the To: line. The second is even worse. I have an Ello account, I’m not waiting. Apparently they pulled their “current user” file and added it to the “waiting user” file and then mailed all of them a notice the accounts were getting turned on, albeit slowly.
The footer of the mail made it clear they knew they were spraying and praying:
September 2014: The Month in Email
- laura
- Oct 1, 2014
September was another busy month for us, but Steve stepped up and wrote a number of really interesting posts on email history, cryptography, and current technical issues in the email landscape.
We started the month with a look at the various RFCs that served as the technical specifications for developing message transfer protocols in the 1970s. It’s really fascinating to look at the evolution of these tools we use every day 40 years later. We followed up with a second post on the origins of network email, which is a great primer (or refresher) on the early days of email.
Steve’s four-part series on cryptography and email started with an in-depth look at how the industry is evolving with respect to encryption and privacy issues. He then introduced us to Alice and Bob (or reintroduced those of us who have been following the adventures of the first couple of cryptography), and described symmetric-key and public-key encryption. His next post described message signing, and how DKIM is used to manage this. He finished up the series with a post on PGP keys.
In industry news: Spamcop is shutting down its email service. There shouldn’t be any major impact on senders, but the post has some specific notes on DMARC implications. We also noted an interesting mail routing suggestion on Twitter, and wrote a post on using Mail.app for this.
In other DMARC news, we wrote about DMARC and report size limits, which might be useful information, depending on your configuration. We also launched a new DMARC tool to help senders understand who is publishing DMARC. Let us know what you think and if you’re finding it useful.
We couldn’t let a month go by without mentioning filters. We looked at a sector we don’t usually discuss, corporate filtering, and went in-depth on a much-misunderstood topic, content filtering.
Finally, Laura offered a webinar on a favorite topic, deliverability, in conjunction with the AMA and Message Systems. If you missed it, you can watch the recorded version here, or just take a peek at some of the reaction via Twitter.
Spamcop mail changes
- laura
- Sep 30, 2014
Spamcop is shutting down it’s email service. While anyone could report spam using Spamcop, the system also provided users email addresses behind the Spamcop filters. This shut down should have no major impact on senders. Email addresses in use will still be accepting email, but that mail will simply be forwarded to another address, instead of users being able to access it through POP or IMAP.
The one problem some senders may have is IF they are solely authenticating through SPF and they are publishing a p=reject DMARC statement. This may result in some of the mail being rejected at the forwarding mail server, like AOL, Yahoo and other services respecting DMARC policy statements.
User forwarded mail will be coming from 68.232.142.20 (esa1.spamcop.iphmx.com) and 68.232.142.151 (esa2.spamcop.iphmx.com). If you don’t want to apply DMARC policy to known forwarded mail, those are the IPs to special case.
DMARC and report size limits
- steve
- Sep 29, 2014
I just saw an interesting observation on the dmarc-discuss mailing list. Apparently some of the larger providers who are implementing DMARC for inbound email may not be handling some of the grubbier corners of the spec perfectly. That’s not surprising at all – early adopters tend to deploy code that implements early versions of the draft specification – but I can see this particular issue tripping up people who are beginning to deploy DMARC for their outbound mail.
DMARC includes the feature of requesting feedback reports about authentication failures – you just include the email address you want them sent to as a mailto: URI in the rua= and ruf= fields:
What about the bots?
- laura
- Sep 26, 2014
M3AAWG published a letter to the FCC addressing the implementation of CSRIC III Cybersecurity Best Practices (pdf link)
The takeaway is that of the ISPs that contribute data to M3AAWG (37M+ users), over 99% of infected users receive notification that they are infected.
I hear from senders occasionally that they are not the problem, bots are the problem and why isn’t anyone addressing bots. The answer is that people are addressing the bot problem.
B2B email filtering
- laura
- Sep 25, 2014
I’ve written about B2B filtering in the past, but I don’t blog too much about corporate filtering overall. The reason for this is that the corporate landscape is a lot broader and less consistent than the consumer space. That makes it much more difficult to tell senders how to handle corporate filtering, because each corporation is different.
But as I think I about it, I realize that’s not necessarily true. In the corporate space there are a few big filtering providers, a couple major hosting systems and a major open source package. While the overall goals of business filtering are slightly different, many businesses have similar goals for their inbound filtering.
Alice and Bob and PGP Keys
- steve
- Sep 24, 2014
Last week Alice and Bob showed how to cryptographically sign messages so that the recipient can be sure that the message came from the purported sender and hasn’t been forged by a third party. They can only do that if they can securely retrieve the senders public key – which means they need to retrieve it from the actual sender, rather than an impostor, and be sure it’s not tampered with en route. How does this work in practice?
If I want to send someone an encrypted email, or I want to verify that a signed email I received from them is valid, I need a copy of their public key (almost certainly their PGP key, in practice). Perhaps I retrieve it from their website, or from a copy they’ve sent me in the past, or even from a public keyserver. Depending on how I retrieved the key, and how confident I need to be about the key ownership, I might want to double check that the key belongs to who I think it does. I can check that using the fingerprint of the key.
A key fingerprint looks like this:
Categories
Tags
- 2010
- 2016
- 2fa
- 419
- 4xx
- 554
- 5xx
- @
- Aarp
- Abacus
- Abandoned
- Aboutmyemail
- Abuse
- Abuse Desk
- Abuse Enforcement
- Abuse Prevention
- Academia
- Accreditation
- Acme
- Acquisition
- Address Book
- Addresses
- Administrivia
- Adsp
- Advanced Delivery
- Advertiser
- Advertising
- Advice
- Affiliate
- Affiliates
- After the Email
- Alerts
- Algorithm
- Alice
- Alignment
- Allcaps
- Alt Text
- AMA
- Amazon
- Amp
- Amsterdam
- Analysis
- Anecdotes
- Anti-Spam
- Anti-Spam Laws
- Anti-Spammers
- Antwort
- AOL
- Appeals
- Appearances
- Appending
- Apple
- Arc
- Arf
- Arrest
- Arrests
- Ascii
- Asides
- Ask Laura
- Askwttw
- Assertion
- Assumptions
- ATT
- Attacks
- Attention
- Attrition
- Audit
- Authentication
- Authentication. BT
- Autonomous
- Award
- B2B
- B2C
- Backhoe
- Backscatter
- Backus-Naur Form
- Banks
- Barracuda
- Barry
- Base64
- Base85
- Bcc
- Bcp
- Bear
- Bears
- Behaviour
- Benchmark
- BESS
- Best Practices
- Bgp
- BIMI
- Bit Rot
- Bitly
- Bizanga
- Black Friday
- Blackfriday
- Blacklist
- Blacklists
- Blast
- Blo
- Block
- Blockin
- Blocking
- Blocklist
- Blocklisting
- Blocklists
- Blocks
- Blog
- Blog Links
- Blogroll
- Blogs
- Bob
- Boca
- Bofa
- Book Review
- Bot
- Botnet
- Botnets
- Bots
- Bounce
- Bounce Handling
- Bounces
- Branding
- Brands
- Breach
- Breaches
- Breech
- Bronto
- Browser
- Bsi
- Bucket
- Bulk
- Bulk Folder
- Bulk Mail
- Business
- Business Filters
- Buying Leads
- Buying Lists
- C-28
- CA
- Caa
- Cabbage
- Cache
- Cadence
- CAH
- California
- Campaign
- CAN SPAM
- Canada
- Candy
- Candycandycandy
- Canonicalization
- Canspam
- Captcha
- Career Developmnent
- Careers at WttW
- Cargo Cult
- Case Law
- Cases
- CASL
- Cat
- Cbl
- CDA
- Cert
- Certification
- CFL
- CFWS
- Change
- Charter
- Cheat
- Cheese
- Choicepoint
- Choochoo
- Christmas
- Chrome
- Cidr
- Cisco
- Civil
- Clear.net
- Clearwire.net
- Cli
- Click
- Click Through
- Click Tracking
- Clicks
- Clickthrough
- Client
- Cloudflare
- Cloudmark
- Cname
- Co-Reg
- Co-Registration
- Cocktail
- Code
- COI
- Comcast
- Comments
- Commercial
- Communication
- Community
- Comodo
- Comparison
- Competitor
- Complaint
- Complaint Rates
- Complaints
- Compliancce
- Compliance
- Compromise
- Conference
- Conferences
- Confirmation
- Confirmed (Double) Opt-In
- Confirmed Opt-In
- Congress
- Consent
- Conservatives
- Consistency
- Constant Contact
- Consultants
- Consulting
- Content
- Content Filters
- Contracts
- Cookie
- Cookie Monster
- COPL
- Corporate
- Cost
- Court Ruling
- Cox
- Cox.net
- Cpanel
- Crib
- Crime
- CRM
- Crowdsource
- Crtc
- Cryptography
- CSRIC
- CSS
- Curl
- Customer
- Cyber Monday
- Czar
- Data
- Data Hygiene
- Data Security
- Data Segmentation
- Data Verification
- DBL
- Dbp
- Ddos
- Dea
- Dead Addresses
- Dedicated
- Dedicated IPs
- Defamation
- Deferral
- Definitions
- Delays
- Delisting
- Deliverability
- Deliverability Experts
- Deliverability Improvement
- Deliverability Summit
- Deliverability Week
- Deliverability Week 2024
- Deliverabiltiy
- DeliverabiltyWeek
- Delivery Blog Carnival
- Delivery Discussion
- Delivery Emergency
- Delivery Experts
- Delivery Improvement
- Delivery Lore
- Delivery News
- Delivery Problems
- Dell
- Design
- Desks
- Dhs
- Diagnosis
- Diff
- Dig
- Direct Mag
- Direct Mail
- Directives
- Discounts
- Discovery
- Discussion Question
- Disposable
- Dk
- DKIM
- Dkimcore
- DMA
- DMARC
- DNS
- Dnsbl
- Dnssec
- Docs
- Doingitright
- Domain
- Domain Keys
- Domain Reputation
- DomainKeys
- Domains
- Domains by Proxy
- Dontpanic
- Dot Stuffing
- Dotcom
- Double Opt-In
- Dublin
- Dyn
- Dynamic Email
- E360
- Earthlink
- Ec2
- Ecoa
- Economics
- ECPA
- Edatasource
- Edns0
- Eec
- Efail
- Efax
- Eff
- Election
- Email Address
- Email Addresses
- Email Change of Address
- Email Client
- Email Design
- Email Formats
- Email Marketing
- Email Strategy
- Email Verification
- Emailappenders
- Emailgeeks
- Emails
- Emailstuff
- Emoji
- Emoticon
- Encert
- Encryption
- End User
- Endusers
- Enforcement
- Engagement
- Enhanced Status Code
- Ennui
- Entrust
- Eol
- EOP
- Epsilon
- Esp
- ESPC
- ESPs
- EU
- Ev Ssl
- Evaluating
- Events
- EWL
- Exchange
- Excite
- Expectations
- Experience
- Expires
- Expiring
- False Positives
- FAQ
- Fathers Day
- Fbl
- FBL Microsoft
- FBLs
- Fbox
- FCC
- Fcrdns
- Featured
- Fedex
- Feds
- Feedback
- Feedback Loop
- Feedback Loops
- Fiction
- Filter
- Filter Evasion
- Filtering
- Filterings
- Filters
- Fingerprinting
- Firefox3
- First Amendment
- FISA
- Flag Day
- Forensics
- Format
- Formatting
- Forms
- Forwarding
- Fraud
- Freddy
- Frequency
- Friday
- Friday Spam
- Friendly From
- From
- From Address
- FTC
- Fussp
- Gabbard
- GDPR
- Geoip
- Gevalia
- Gfi
- Git
- Giveaway
- Giving Up
- Global Delivery
- Glossary
- Glyph
- Gmail
- Gmails
- Go
- Godaddy
- Godzilla
- Good Email Practices
- Good Emails in the Wild
- Goodmail
- Google Buzz
- Google Postmaster Tools
- Graphic
- GreenArrow
- Greylisting
- Greymail
- Groupon
- GT&U
- Guarantee
- Guest Post
- Guide
- Habeas
- Hack
- Hacking
- Hacks
- Hall of Shame
- Harassment
- Hard Bounce
- Harvesting
- Harvey
- Hash
- Hashbusters
- Headers
- Heartbleed
- Hearts
- HELO
- Help
- Henet
- Highspeedinternet
- Hijack
- History
- Holiday
- Holidays
- Holomaxx
- Hostdns4u
- Hostile
- Hostname
- Hotmail
- How To
- Howto
- Hrc
- Hsts
- HTML
- HTML Email
- Http
- Huey
- Humanity
- Humor
- Humour
- Hygiene
- Hypertouch
- I18n
- ICANN
- Icloud
- IContact
- Identity
- Idiots
- Idn
- Ietf
- Image Blocking
- Images
- Imap
- Inbox
- Inbox Delivery
- Inboxing
- Index
- India
- Indiegogo
- Industry
- Infection
- Infographic
- Information
- Inky
- Inline
- Innovation
- Insight2015
- Integration
- Internationalization
- Internet
- Intuit
- IP
- IP Address
- Ip Addresses
- IP Repuation
- IP Reputation
- IPhone
- IPO
- IPv4
- IPv6
- Ironport
- Ironport Cisco
- ISIPP
- ISP
- ISPs
- J.D. Falk Award
- Jail
- Jaynes
- JD
- Jobs
- Json
- Junk
- Juno/Netzero/UOL
- Key Rotation
- Keybase
- Keynote
- Kickstarter
- Kraft
- Laposte
- Lavabit
- Law
- Laws
- Lawsuit
- Lawsuits
- Lawyer
- Layout
- Lead Gen
- Leak
- Leaking
- Leaks
- Legal
- Legality
- Legitimate Email Marketer
- Letsencrypt
- Letstalk
- Linked In
- Links
- List Hygiene
- List Management
- List Purchases
- List the World
- List Usage
- List-Unsubscribe
- Listing
- Listmus
- Lists
- Litmus
- Live
- Livingsocial
- London
- Lookup
- Lorem Ipsum
- Lycos
- Lyris
- M3AAWG
- Maawg
- MAAWG2007
- Maawg2008
- MAAWG2012
- MAAWGSF
- Machine Learning
- Magill
- Magilla
- Mail Chimp
- Mail Client
- MAIL FROM
- Mail Privacy Protection
- Mail Problems
- Mail.app
- Mail.ru
- Mailboxes
- Mailchimp
- Mailgun
- Mailing Lists
- Mailman
- Mailop
- Mainsleaze
- Maitai
- Malicious
- Malicious Mail
- Malware
- Mandrill
- Maps
- Marketer
- Marketers
- Marketing
- Marketo
- Markters
- Maths
- Mcafee
- Mccain
- Me@privacy.net
- Measurements
- Media
- Meh
- Meltdown
- Meme
- Mentor
- Merry
- Message-ID
- Messagelabs
- MessageSystems
- Meta
- Metric
- Metrics
- Micdrop
- Microsoft
- Milter
- Mime
- Minimal
- Minshare
- Minute
- Mit
- Mitm
- Mobile
- Models
- Monitoring
- Monkey
- Monthly Review
- Mpp
- MSN/Hotmail
- MSN/Hotmail
- MTA
- Mua
- Mutt
- Mx
- Myths
- Myvzw
- Needs Work
- Netcat
- Netsol
- Netsuite
- Network
- Networking
- New Year
- News
- News Articles
- Nhi
- NJABL
- Now Hiring
- NTP
- Nxdomain
- Oath
- Obituary
- Office 365
- Office365
- One-Click
- Only Influencers
- Oops
- Opaque Cookie
- Open
- Open Detection
- Open Rate
- Open Rates
- Open Relay
- Open Tracking
- Opendkim
- Opens
- Openssl
- Opt-In
- Opt-Out
- Optonline
- Oracle
- Outage
- Outages
- Outblaze
- Outlook
- Outlook.com
- Outrage
- Outreach
- Outsource
- Ownership
- Owning the Channel
- P=reject
- Pacer
- Pander
- Panel
- Password
- Patent
- Paypal
- PBL
- Penkava
- Permission
- Personalities
- Personalization
- Personalized
- Pgp
- Phi
- Philosophy
- Phish
- Phishers
- Phishing
- Phising
- Photos
- Pii
- PIPA
- PivotalVeracity
- Pix
- Pluscachange
- Podcast
- Policies
- Policy
- Political Mail
- Political Spam
- Politics
- Porn
- Port25 Blocking
- Postfix
- Postmaster
- Power MTA
- Practices
- Predictions
- Preferences
- Prefetch
- Preview
- Primers
- Privacy
- Privacy Policy
- Privacy Protection
- Private Relay
- Productive Mail
- Promotions
- Promotions Tab
- Proofpoint
- Prospect
- Prospecting
- Protocols
- Proxy
- Psa
- PTR
- Public Suffix List
- Purchased
- Purchased Lists
- Purchases
- Purchasing Lists
- Questions
- Quoted Printable
- Rakuten
- Ralsky
- Rant
- Rate Limiting
- Ray Tomlinson
- Rc4
- RDNS
- Re-Engagement
- Read
- Ready to Post
- Readytopost
- Real People
- Realtime Address Verification
- Recaptcha
- Received
- Receivers
- Recipient
- Recipients
- Redirect
- Redsnapper
- Reference
- Registrar
- Registration
- Rejection
- Rejections
- Rejective
- Relationship
- Relevance
- Relevancy
- Removals
- Render Rate
- Rendering
- Replay
- Repost
- Repudiation
- Reputation
- Requirements
- Research
- Resources
- Responsive
- Responsive Design
- Responsys
- Retail
- Retired Domains
- Retro
- Return Path
- Return Path Certified
- ReturnPath
- Reunion.com
- Reverse Dns
- RFC
- RFC2047
- RFC2821/2822
- RFC5321/5322
- RFC5322
- RFC8058
- RFC821/822
- RFCs
- Roadr
- RoadRunner
- Rodney Joffe
- ROKSO
- Role Accounts
- Rollout
- RPost
- RPZ
- Rule 34
- Rules
- Rum
- Rustock
- S.1618
- SaaS
- Sales
- Salesforce
- Sass
- SBCGlobal
- Sbl
- Scam
- Scammers
- Scams
- Scanning
- Scraping
- Screamer
- Screening
- Script
- Sec
- Secure
- Security
- Segmentation
- Selligent
- Send
- Sender
- Sender Score
- Sender Score Certified
- Senderbase
- Senderid
- Senders
- Senderscore
- Sendgrid
- Sending
- Sendy
- Seo
- Service
- Services
- Ses
- Seth Godin
- SFDC
- SFMAAWG2009
- SFMAAWG2010
- SFMAAWG2014
- Shared
- Shell
- Shouting
- Shovel
- Signing
- Signups
- Silly
- Single Opt-In
- Slack
- Slicing
- Smarthost
- Smiley
- Smime
- SMS
- SMTP
- Snds
- Snowshoe
- Soa
- Socia
- Social Media
- Social Networking
- Soft Bounce
- Software
- Sony
- SOPA
- Sorbs
- Spam
- Spam Blocking
- Spam Definition
- Spam Filtering
- Spam Filters
- Spam Folder
- Spam Law
- Spam Laws
- Spam Reports
- Spam Traps
- Spam. IMessage
- Spamarrest
- Spamassassin
- Spamblocking
- Spamcannibal
- Spamcon
- Spamcop
- Spamfiltering
- Spamfilters
- Spamfolder
- Spamhaus
- Spamhause
- Spammer
- Spammers
- Spammest
- Spamming
- Spamneverstops
- Spamresource
- Spamtrap
- Spamtraps
- Spamza
- Sparkpost
- Speaking
- Special Offers
- Spectre
- SPF
- Spoofing
- SproutDNS
- Ssl
- Standards
- Stanford
- Starttls
- Startup
- State Spam Laws
- Statistics
- Storm
- Strategy
- Stunt
- Subject
- Subject Lines
- Subscribe
- Subscriber
- Subscribers
- Subscription
- Subscription Process
- Success Stories
- Suing
- Suppression
- Surbl
- Sureclick
- Suretymail
- Survey
- Swaks
- Syle
- Symantec
- Tabbed Inbox
- Tabs
- Tagged
- Tagging
- Target
- Targeting
- Techincal
- Technical
- Telnet
- Template
- Tempo
- Temporary
- Temporary Failures
- Terminology
- Testing
- Text
- Thanks
- This Is Spam
- Throttling
- Time
- Timely
- TINS
- TLD
- Tlp
- TLS
- TMIE
- Tmobile
- Too Much Mail
- Tool
- Tools
- Toomuchemail
- Tor
- Trademark
- Traffic Light Protocol
- Tragedy of the Commons
- Transactional
- Transition
- Transparency
- Traps
- Travel
- Trend/MAPS
- Trend Micro
- Trend/MAPS
- Trigger
- Triggered
- Troubleshooting
- Trustedsource
- TWSD
- Txt
- Types of Email
- Typo
- Uce
- UCEprotect
- Unblocking
- Uncategorized
- Undisclosed Recipients
- Unexpected Email
- Unicode
- Unroll.me
- Unsolicited
- Unsubcribe
- Unsubscribe
- Unsubscribed
- Unsubscribes
- Unsubscribing
- Unsubscription
- Unwanted
- URIBL
- Url
- Url Shorteners
- Usenet
- User Education
- Utf8
- Valentine's Day
- Validation
- Validity
- Value
- Valueclick
- Verification
- Verizon
- Verizon Media
- VERP
- Verticalresponse
- Vetting
- Via
- Video
- Violence
- Virginia
- Virtumundo
- Virus
- Viruses
- Vmc
- Vocabulary
- Vodafone
- Volume
- Vzbv
- Wanted Mail
- Warmup
- Weasel
- Webinar
- Webmail
- Weekend Effect
- Welcome Emails
- White Space
- Whitelisting
- Whois
- Wiki
- Wildcard
- Wireless
- Wiretapping
- Wisewednesday
- Women of Email
- Woof
- Woot
- Wow
- Wtf
- Wttw in the Wild
- Xbl
- Xfinity
- Xkcd
- Yahoo
- Yahoogle
- Yogurt
- Zoidberg
- Zombie
- Zombies
- Zoominfo
- Zurb