Dodgy PDF handling at Gmail
We sent out some W-9s this week. For non-Americans and those lucky enough not to have to deal with IRS paperwork those are tax forms.
They’re simple single page forms with the company name, address and tax ID numbers on them. Because this is the 21st Century we don’t fill them in with typewriters and snail mail them out, we fill in a form online at the IRS website which gives us PDFs to download that we then send out via email.
We started to get replies from people we’d sent them to that we hadn’t included the tax ID number. Which was odd, because it was definitely there in the PDFs we’d sent.
The reports of missing numbers came from Google Apps users, so we sent a copy to one of our Gmail addresses to see. Sure enough, when you click on the attachment it’s mostly there, but some of the digits of the tax ID number are missing.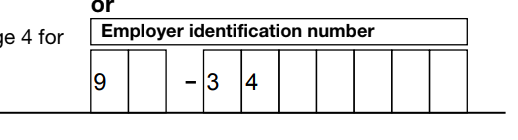
And all the spaces have been stripped from our address.
The rest of the form looked fine, but the information we’d entered was scrambled. Downloading the PDF from Gmail and displaying it – everything is there, and in the right place.
Weird. After a brief “Are gmail hiding things that look like social security numbers?” detour I realized that the IRS website was probably generating the customized forms using PDF annotations.
PDF is a very powerful, but very complex, file format. It’s not just an image, it’s a combination of different elements – images, lines, vector artwork, text, interactive forms, all sorts of things – bundled together into a single file. And you can add elements to an existing PDF file to, for example, overlay text on to it. These “annotations” are a common way to fill in a PDF form, by adding text in the right place over the top of an existing template PDF.
I cracked the PDF open with some forensics tools and sure enough, the IRS had generated the PDF form using annotations.
<< /Type /Annot /DV (Palo Alto, CA) /T (topmostSubform[0].Page1[0].Address[0].f1_8[0]) /Rect [ 57.6 539.968 388.8 553.969 ] /AP 81 0 R /FT /Tx /DA (/Helvetica-Bold 9 Tf 0 g)
And the Gmail PDF viewer isn’t rendering that annotated text correctly.
I’ve filed a bug sent feedback to Google, so hopefully it’ll be fixed. Meanwhile, if you’re sending customized content to recipients using PDF you should probably check that it renders correctly when previewed in Gmail.