Another way Gmail is different
I was answering a question on Mailop earlier today and had one of those moments of clarity. I finally managed to articulate one of the things I’ve known about Gmail, but never been able to explain. See, Gmail has never really put a lot of their filtering on the SMTP transaction and IP reputation. Other ISPs do a lot of the heavy lifting with IP filters. But not Gmail.
While I was writing the answer I realized something. Gmail was a late entrant into the email space. AOL, Hotmail, Yahoo, even the cable companies, were providing email services in the 90s. When spam started to be a problem, they started with IP based blocking. As technology got better and content filtering became viable, improvements were layered on top of IP based blocking.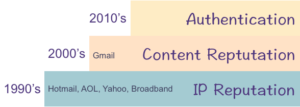
Gmail didn’t enter the mailbox market until the 2000’s. When they did, they had money, lots of hardware, and internal expertise to do content filtering. They didn’t start with IP based filtering, so their base is actually content filtering. Sure, there were some times when they’d push some mail away from the MTAs, but most of their filtering was done after the SMTP transaction. The short version of this is I never really pay any attention to IP reputation when dealing with Gmail. It’s just another factor. Unless you’re blocked and if you get blocked by Gmail, wow, you really screwed up.
Gmail does, of course, do some IP based blocking. But in my experience IP filters are really only turned against really egregious spam, phishing and malicious mail. Most email marketers reading my blog won’t ever see IP filters at Gmail because their mail is not that bad.
Other companies aren’t going to throw away filters that are working, so the base of their filters are IPs. But Google never had that base to work from. Their base is content filters, with some IP rep layered on top of that.
That’s a big reason Gmail filters are different from other filters.