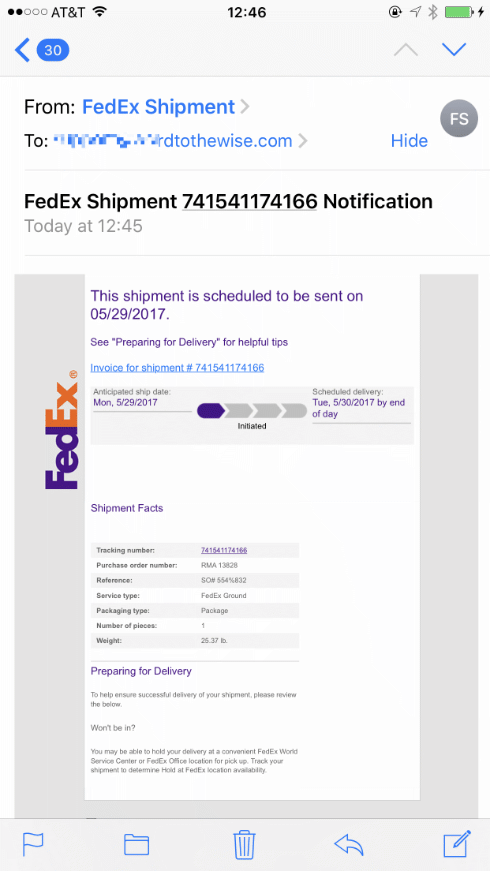
We know that legitimate email sent with valid SPF and a DKIM signature often breaks in transit.
SPF will fail any time mail is forwarded – via a mailing list, a forwarding service used by the recipient, or just ad-hoc forwarding.
DKIM will fail any time the message is modified in transit. That can be obviously visible changes, such as a mailing list tagging a subject header or adding a footer to the body. It can also be less obvious changes, such as intermediate MTAs wrapping lines that are too long, reencoding content or repackaging the message altogether – perhaps when delivering from a mailserver that is 8BITMIME compliant to one that isn’t.

(This image has absolutely nothing to do with email authentication, but searching for stock photography about email or authentication or chains or, well, pretty much anything like that leads to horribly depressing corporate imagery. So, no. Have something colourful and optimistic instead.)
As SPF and DKIM are typically used, none of this is much of a problem. A message being authenticated provides a little extra information to the receiving mailserver, and the domain attached to the authentication can be used to look up a senders reputation, giving a potential boost to the chances of the mail being sent to the inbox. If the authentication is broken, though, the mail will still be judged on it’s merits – is it coming from an IP address that’s a source of good mail, does the content look legitimate, and all the other things a spam filter looks at.
That authentication is a (potentially big) positive signal, but lack of authentication isn’t really any signal at all is why SPF and DKIM being fragile wasn’t an issue. SPF and DKIM are positive assertions – “IF this mail IS authenticated THEN IT IS from me”.
That changed when DMARC became popular, though.
DMARC allows the owner of a domain to say “We send no mail that is not authenticated, and we promise that none of that authentication will be broken in transit”. DMARC is a negative assertion – “IF this mail IS NOT authenticated THEN it IS NOT from me”. It converts the absence of a positive assertion into a negative assertion.
This isn’t the first attempt to layer a “we authenticate everything” negative assertion on top of fragile email authentication. SPF did it, with the -all flag (which is universally ignored, leaving SPF purely as a positive assertion). DomainKeys did it, with DomainKeys policy records (which you occasionally still see published, but were never really used to reject mail). DKIM did it with ADSP – which didn’t see much use either.
The reason none of them were used much is because even when senders were telling the truth about “we send no email that is not authenticated” they were always lying, to varying degrees, about “none of the authentication will be broken in transit”.
If your domain that is solely used for bulk email. If it’s never for used mail sent by human beings, not even customer support employees. If it’s a newly created domain with no legacy usage that only sends email from a very tightly controlled infrastructure. If you only send email that’s been created via a well implemented message composition pipeline that ensures the content of the is not just RFC compliant but also “well formed”, with short lines, simple widely implemented encoding, vanilla mime structure and so on. And it’s sent out via conservatively configured smarthosts that deliver directly to the end recipients MX. And if you know that the demographics of your recipients are such that the minority that are forwarding that mail elsewhere (e.g. from their Yahoo account to their Google account or via an alumni mail alias) is a small enough group that you don’t care about them…
If all of those things are true, then your domain is going to be able to deploy DMARC pretty easily and safely. If not, though, how can you tell?
That’s the place where DMARC improves over it’s predecessors. It allows you not only to publish a DMARC policy record in test mode, so it’s not actually used to filter your mail (well, mostly, but that’s a longer story) but also to ask recipients to notify you of mail that seems to be from you but which isn’t authenticated.
You can publish a “p=none” DMARC record with notification addresses in it and wait and see what happens. You’ll get notification of mail that has your domain in the From: field but which isn’t authenticated.
As a first round of action that lets you see where you’re sending email from that you didn’t know about. Sysadmin notification email. That marketing splinter group in Sasketchwan. The outsourced survey company.
Once you’ve cleaned all that up, and made sure everyone is authenticating their mail then you can look at what’s left. The next step is likely to be mistakes you’re making in authentication or message composition that’s causing some of your mail – typically depending on content, and source and recipient domain – to become unauthenticated. Clean that up, make sure all your message composition is squeaky clean, make sure employees aren’t sending mail using that domain in ways you don’t authorize (interacting with mailing list, for example).
By that point you’ll have reduced the torrent of reports you’re getting to two types. One is mail that you send that has it’s authentication broken in transit through some process you have no control over. The other type is mail that has your domain in the “From” field but which you didn’t send. Some of that may be legitimate use of your domain by your employees, such as forward-to-a-friend services, signing up for document delivery via email, third-party notification services. By deploying DMARC you are declaring all that sort of usage to be illegitimate, and you’ll need to get all your employees to stop doing it (or, at least, know that it’s going to stop working). The rest of it is likely a mix of spam and phishing mail. The spam, that’s just using your domain in random from addresses, you probably don’t care about. The phishing you do.
You’ve finally cleaned up your mail infrastructure and policies enough to gather the data you need. How much of my legitimate email will have it’s authentication broken (and hence be silently thrown away by DMARC)? And how much hostile phishing mail is targeting my users (and using the exact domain you are)?
Then you have the information you need to make an informed decision as to how badly deploying DMARC will break your legitimate use of email (after you’ve done everything you can to minimize that) and some idea of whether it will provide you any benefit, at least in the shorter term.
That testing phase, where senders can use other peoples mail infrastructure to investigate their sending practices, gradually fix any problems and finally gather some metrics is what made gave the developers of the DMARC spec confidence that it wouldn’t break things, and made it much more deployable than previous approaches to negative assertion.
On Monday, how all that optimistic reasoning went to hell, what it broke and how we’re trying to fix it.
Read More