It's not about the spamtraps
- laura
- September 8, 2015
- Best practices
I’ve talked about spamtraps in the past but they keep coming up in so many different discussions I have with people about delivery that I feel the need to write another blog post about them.
Spamtraps are …
… addresses that did not or could not sign up to receive mail from a sender.
… often mistakenly entered into signup forms (typos or people who don’t know their email addresses).
… often found on older lists.
… sometimes scraped off websites and sold by list brokers.
… sometimes caused by terrible bounce management.
… only a symptom …
… of a bigger problem with address collection.
Removing spamtraps …
… just means you’ve removed the spamtraps you know about.
… may mean you have a spamtrap free list …
… until you start adding new addresses to it.
… does not fix mail going to addresses belonging to other people.
… does not guarantee good delivery.
… ignores the underlying issues.
Why do people take spamtraps so seriously?
A lot of this is historical and some of it is to avoid arguments. Just about any sender, when told they’re sending mail to someone who didn’t ask for it will respond “But we only send opt-in mail! That person is wrong! They signed up!!” I’ve had this happen to me more times than I can count.
I’ve even had clients come to me in the past where I’ve been able to dig into my own mailbox to affiliate spam. This is always a fun conversation.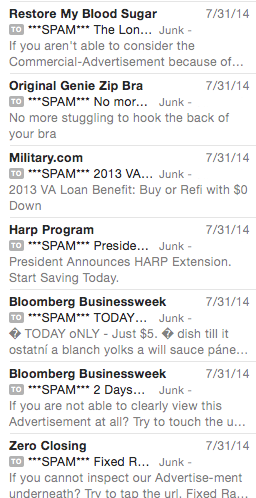 Me: Here are a dozen examples of the mail your affiliates sent to me in the last month.
Me: Here are a dozen examples of the mail your affiliates sent to me in the last month.
Client: All our affiliates send opt-in mail. They’ve assured us of this.
Me: This is an email address only ever published on a website / not used since 2001 to sign up for anything / untagged so it’s not something I would have given them.
Client: Our vendors say you’re wrong. Would you like to hop on a call with them so they can tell you when you opted in?
The calls have happened and vendors have argued with me about whether or not I opted in to receive stuff from them. It tends to end up them claiming I opted in to mail and me telling them I did not. Sometimes they tell me I just forgot – except all my actual opt ins are tagged addresses and have been since roughly 1999, so if you’re not mailing a tagged address, I never gave it to you. Sometimes they tell me I opted in to some company they purchased back in the late 90s and therefore they had permission to send to me.
The discussions are never productive. They are so fixated on their business story, that they will duck and weave and tell me I’m wrong about the spam they are sending me.
This is why people focus on spamtraps!
With spamtraps there isn’t the discussion of whether or not someone signed up. There’s no account owner, no one who has this address and could have signed up. Even in the case of recycled traps, the addresses generally bounced for a while telling senders there was no account owner there. Focusing on spamtraps on a list deflects the back and forth argument about whether or not the sender has permission to send mail they’re sending.
But spamtraps aren’t the problem!
In fact, I was just talking to one of the Spamhaus volunteers who told me “I hate the modern day focus on traps.” I agree. We focus on traps because it deflects and diffuses a lot of the arguments about whether or not someone opted in. But that means we don’t address a lot of real issues, either. If there are spamtraps on a list, then that list has problems. Focusing on removing the traps doesn’t resolve the problems, it just focuses on the traps. That tends to lead to a cleanup strategy that doesn’t do what the sender thinks it does.
Spamtraps are the symptom!
If there are spamtraps on a list, then there are also addresses that go to a person who never opt-in on that same list. Focusing on fixing the problems that led to the spamtraps getting on the list then cleaning off addresses that aren’t performing leads to better overall delivery and fewer problems. Focusing on getting rid of spamtraps may, but may not, fix a SBL listing. Maybe. But it’s my experience that fixing a SBL listing may only resolve a small fraction of delivery problems. Getting off the SBL by trying to address spamtraps, will not fix bulk foldering or temp fails are major webmail providers.
Focusing on improving overall list hygiene and really making sure that mail is wanted and expected by the recipients generally will resolve both the SBL listing and fix the other delivery problems that are happening because of poor data and poor list hygiene.
I’ve written about spamtraps before.
- Only spamtraps matter, or do they?
- Spamtraps, again.
- Spamtraps are not the problem
- Spamtraps mean your list is bad
- Spamtraps: should you care?
- A brief guide to spamtraps (I can’t believe this is almost 4.5 year old post)
- Typo traps
- The true facts of spam traps and typo traps
- More on spamtraps
- We only mail people who sign up!